Female Pattern Alopecia
Clinical Presentation (1)
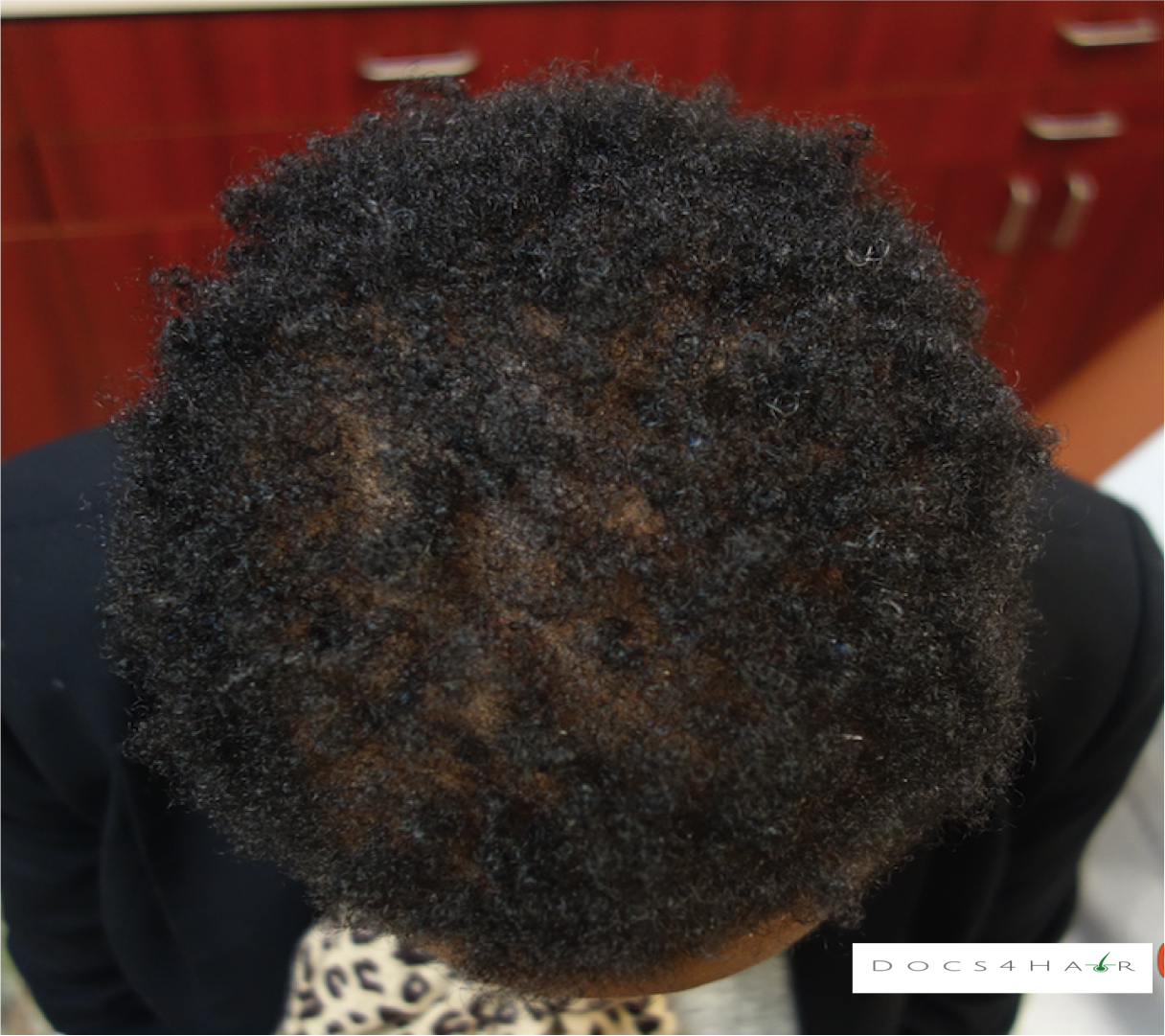
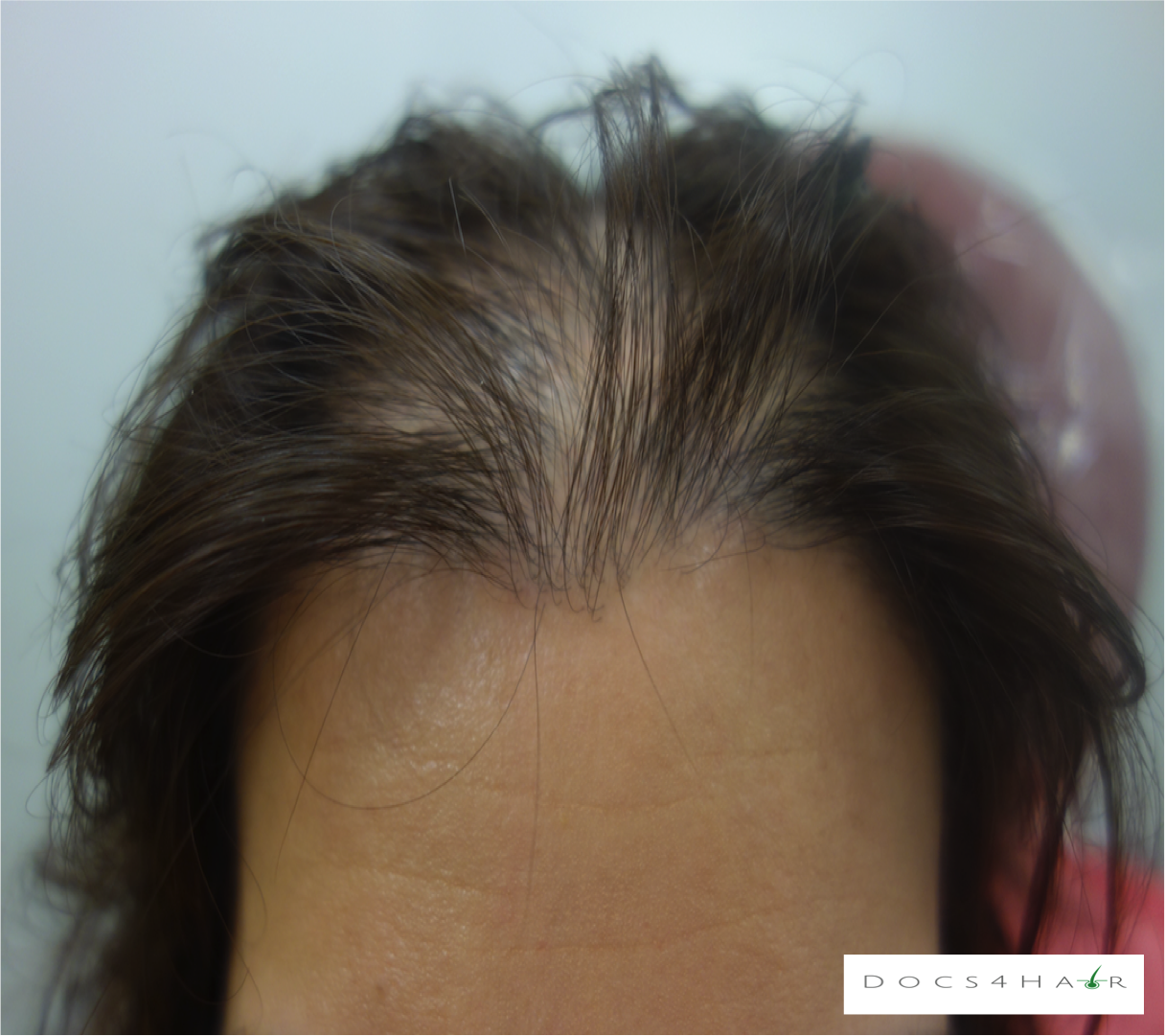
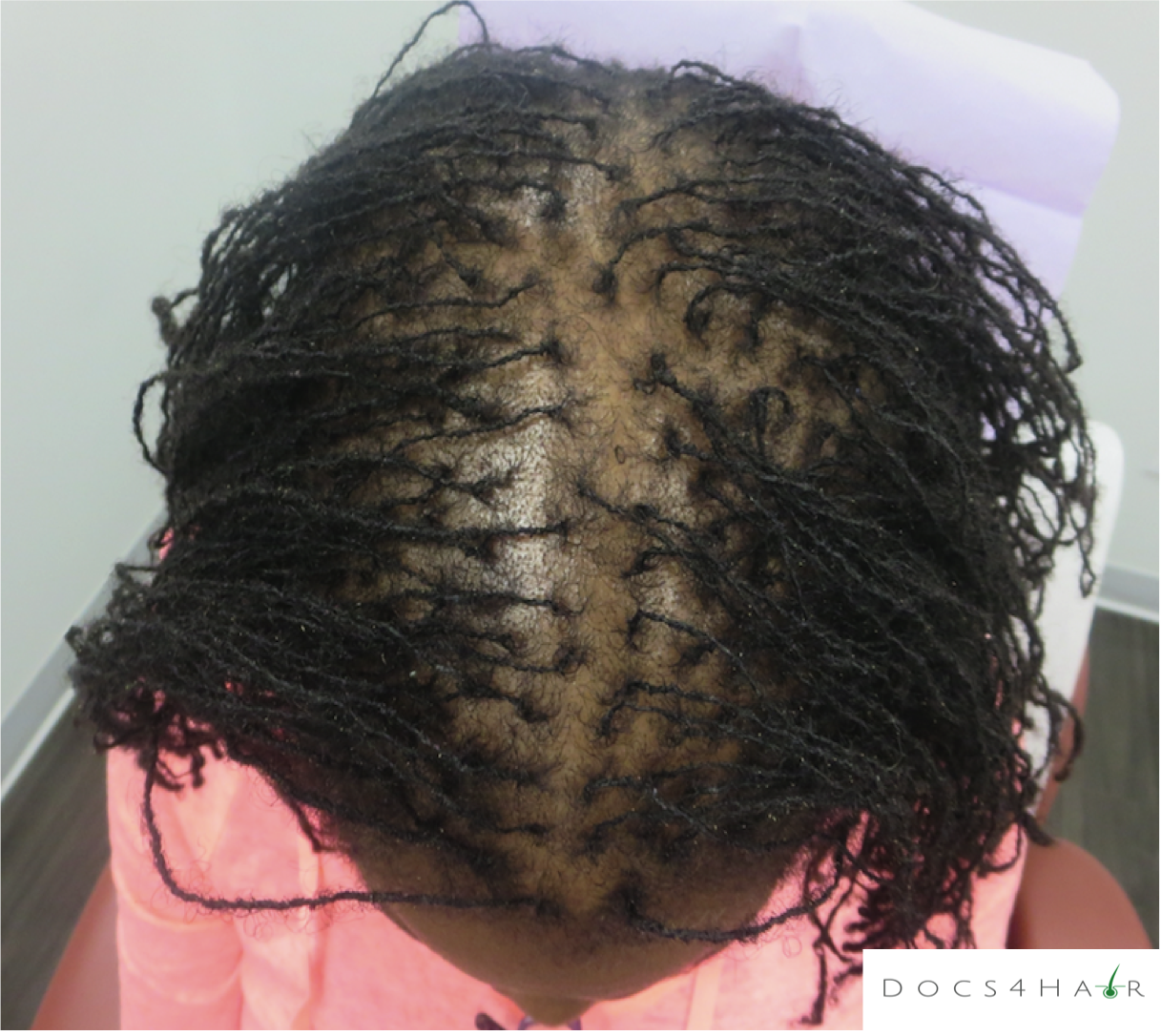
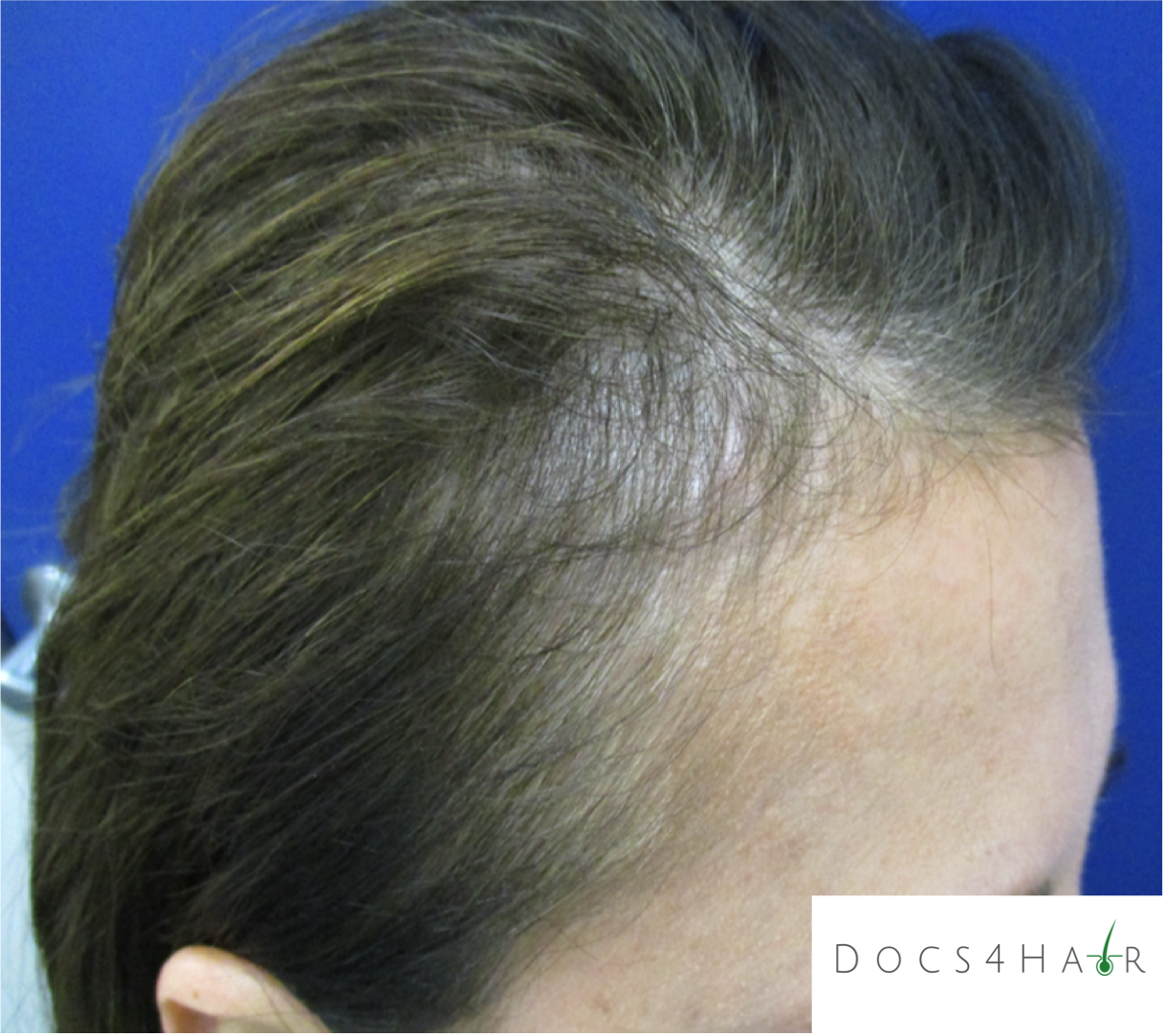
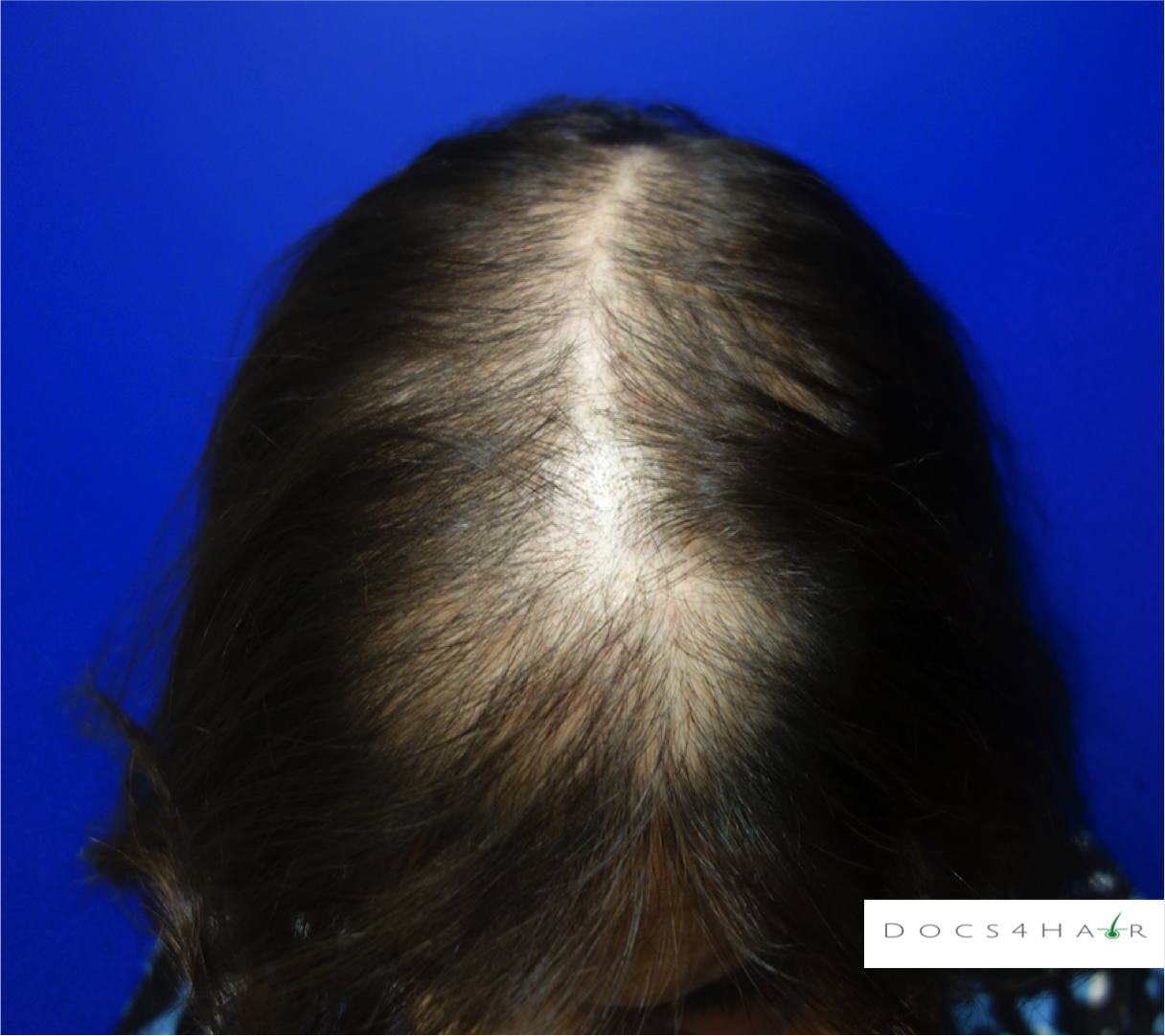
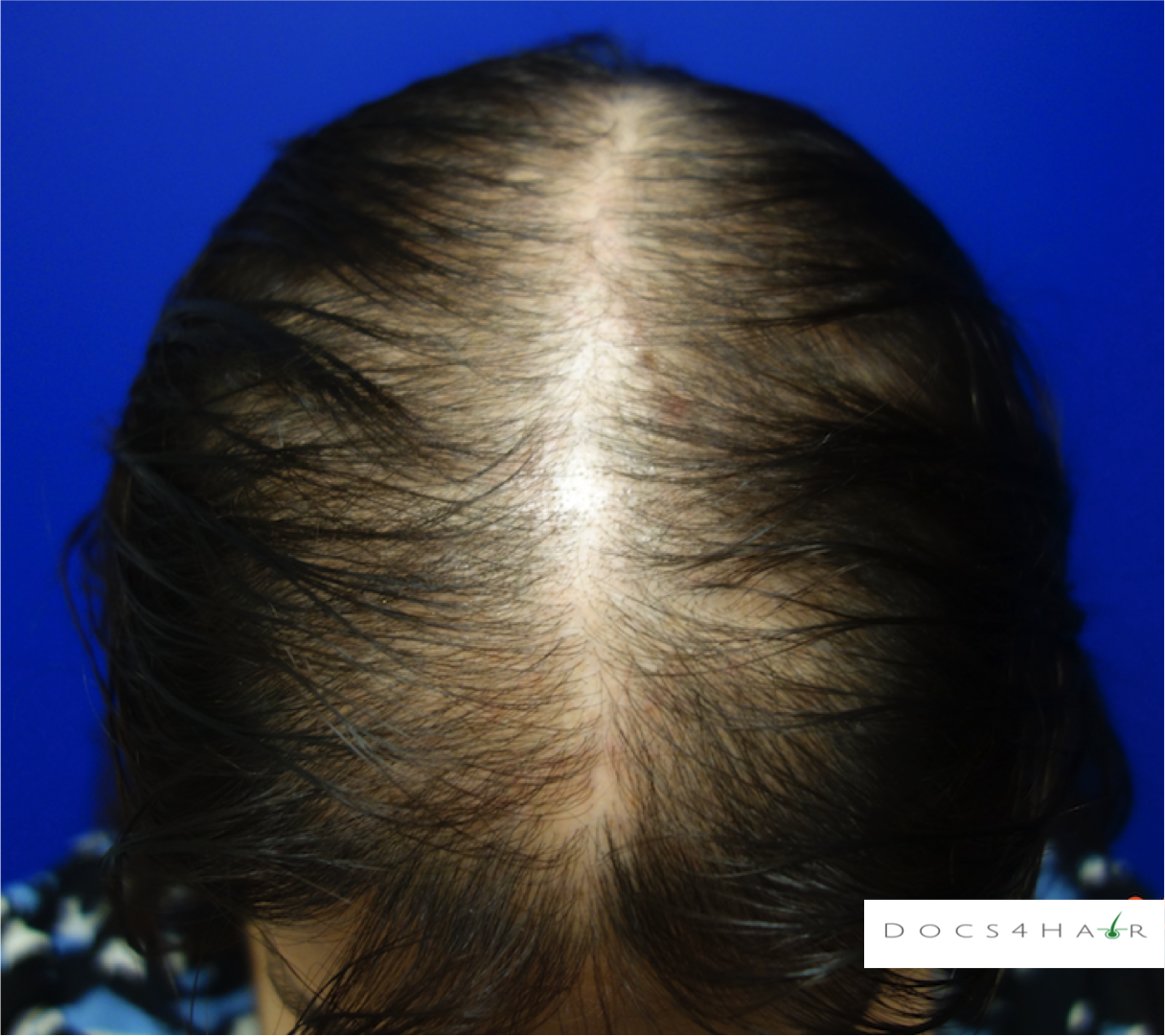
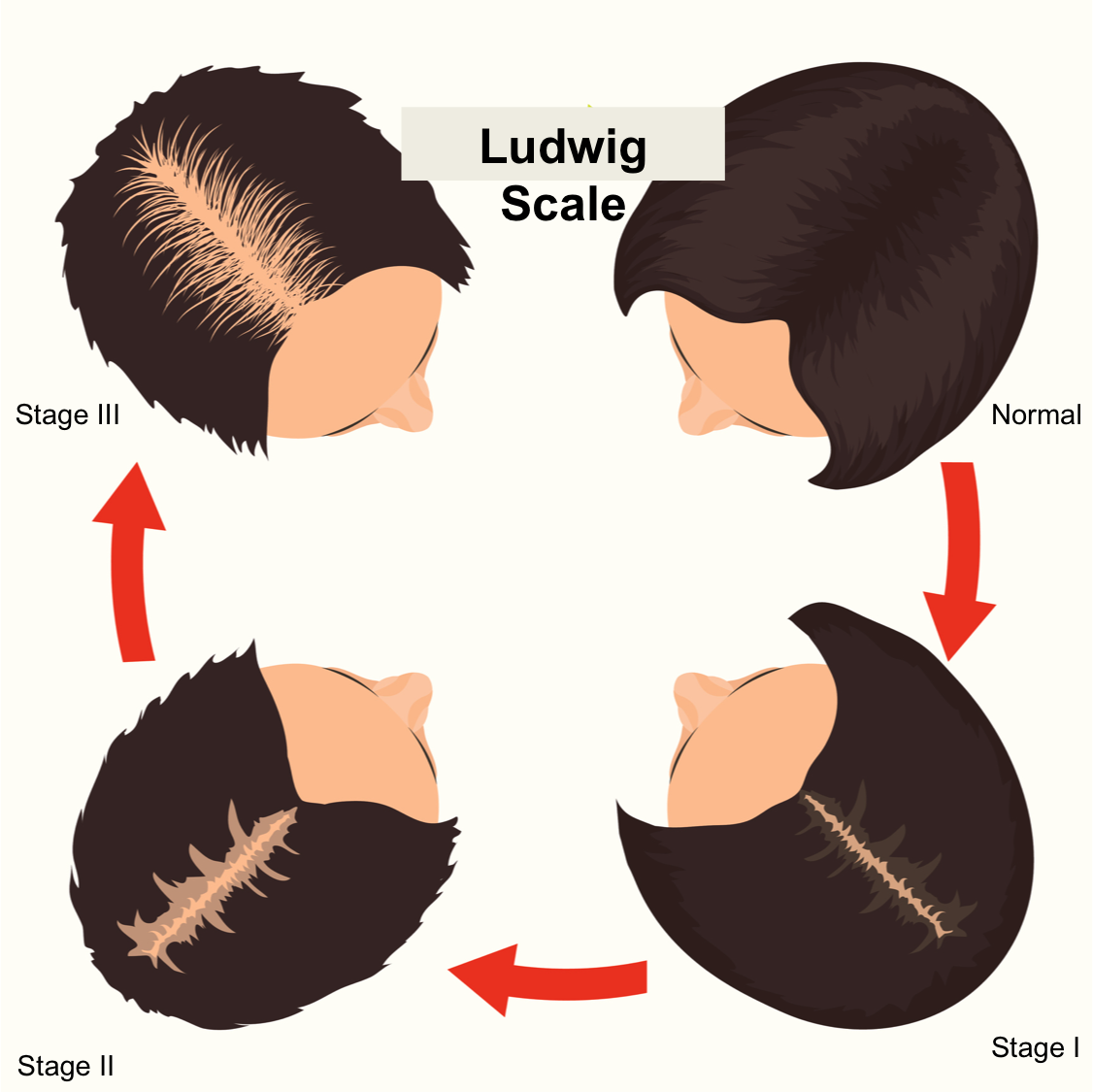
Female pattern alopecia (FPA)/ androgenetic alopecia is a chronic progressive non-scarring hair loss condition usually occurring in a pattern. It typically presents as a diffuse hair loss in the mid and frontal regions of the scalp with preservation of the frontal hairline. The deep recession of the hairline (fronto-temporal), as seen in men, rarely occurs . The Ludwig scale is used to classify the stages of progression.
Epidemiology(1, 2)
Most common hair loss disorder affecting women. Affects up to 56% of Caucasian women by the age of 70.
Causes (1, 3)
The exact cause of FPA is unknown and is likely multifactorial. There are several proposed mechanisms for MPA including:
Genetic predisposition
Hormone abnormalities (uncertain, local vs systemic?)
Elevated androgen levels or elevated androgen/estrogen ratio (uncommon)
Androgen sensitivity in the follicle leading to miniaturization (hairs shrink in size over time to small, thin, short vellus hairs, eventually leaving a bald scalp)
Increased numbers of telogen (resting) follicles and shorted anagen (growth) phase
“Micro-inflammation”: possible
Diagnosis (1)
FPA is diagnosed via history, clinical scalp exam, and dermoscopic evaluation. Rarely, scalp biopsies are performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Clinical Imitators (Differential Diagnosis)(1)
Alopecia areata, lichen planopilaris, central centrifugal cicatrial alopecia, frontal fibrosing alopecia, telogen effluvium, trichotillomania
Associated Conditions (1, 3)
Metabolic disease (obesity, insulin resistance, polycystic ovarian syndrome, cardiovascular disease, hyperprolactinaemia and raised aldosterone levels)
Treatment Options (2, 3, 4, 5)
Treatment (single or combination) depends stage/ extent of the condition.
Anti-androgens: 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (oral finasteride- postmenopausal women, some improvement at higher doses (5mg), use is controversial, long-term side effects unknown), oral spironolactone, topical ketoconazole
Post Finasteride Syndrome: To date, there are no studies to support the existence of persistent post-use sexual or mental health side effects (6)
Growth stimulants: Minoxidil (anagen phase promoter- topical/ oral)
Phototherapy: Low level light therapy
Hair Restoration: Platelet rich plasma, hair transplantation
Scalp camouflage: Scalp micro-pigmentation, hair fibers, color stick, and scalp prosthesis (e.g., customized wigs).
Essential oils: rosemary essential oil (7)
Nutritional supplementation